Windows Task Manager is a powerful system-monitoring tool that comes built-in with Microsoft Windows operating systems. It provides real-time information about the various processes, applications, and services running on your computer.
When Windows 11 was released, Task Manager got a fresh new look, with new features that can help you actually reduce how much power is drawn from your device. As is the case with many applications, there’s a lot more to Task Manager than meets the eye.
If you want to make the most out of Task Manager, here are five must-know features you should look at and things you should do.
Navigating to Windows Task Manager
Before moving on to what’s available, you should first know how to access Windows Task Manager. The fastest way to get to it is by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Alternatively, you can use Ctrl + Alt + Del, then select Task Manager from the list of options.
If you don’t want to use a keyboard shortcut, you can navigate to the Start menu and select Task, or find it from the list of options.
Finally, with the most up-to-date version of Windows 11, you can right-click on the taskbar on your device, and then select Task Manager from the list of options.
1. Manage Startup processes

When you download and install an app on your device, there’s a high chance the process will start automatically whenever you turn on your PC or laptop. With multiple apps all launching at the same time, your computer can feel sluggish, especially if you don’t need to use the apps that often.
Using Task Manager, you can decide which programs start when your computer turns on. For instance, you might not want Skype to launch every time your computer does. To manage your startup apps via Task Manager, simply open Task Manager and then select Startup Apps from the left-hand toolbar. You can also access Startup Apps via Windows Settings.
2. Access performance and resources data

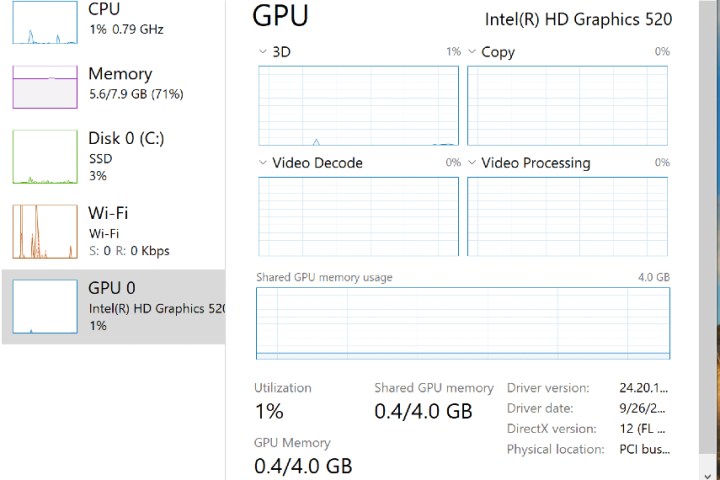
Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that provides detailed insights into your computer’s performance and resource usage. Once you’ve launched Task Manager, there are various tabs you can explore such as Performance, which can give you a better understanding of how your computer is using the resources available.
The Performance tab showcases real-time graphs for CPU, memory, disk, GPU, and network usage. You can observe how each resource is being utilized over time. Using the dotted menu option, you can also expand the Performance tab to access your computer’s Resource Monitor. This offers a more detailed breakdown of resource usage, meaning you can dig deeper into your system’s health, troubleshoot performance issues, or manage processes.
You can also copy details of any tab in Task Manager by right-clicking and selecting Copy or using Ctrl + C. This is useful for sharing information or storing it for analysis.
3. Search online
It’s not uncommon to find processes in Task Manager that you don’t recognize. Even tech-savvy users might feel dumbfounded over a particular process that, without digging deeper into it, may seem suspicious. While most processes are likely to be legitimate, there’s no harm in investigating something that doesn’t sit right.
If you come across a process you want further information on, you can right-click it and select the option to Search online. A Microsoft Bing search will launch in your browser, allowing you to view the results. It’s a simple process that could uncover something that shouldn’t be on your computer, or offer reassurance about something that should.
4. More columns, more detail

When you first open Task Manager, you’ll be presented with a small selection of data, e.g. CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network. But what if you want to view more data than what’s already there? If you right-click on any of the existing data columns, you’ll find a list of other options you can add, such as Publisher, Process Name, GPU, and more.
Not all of the data will be useful all of the time, but these extra columns can offer added insight for troubleshooting purposes. It’s a handy setting to be able to access, and something that works in the Startup Apps tab, as well as Processes.
5. Efficiency mode

One of the aforementioned columns you can add to Task Manager is Power Usage. But it deserves a little more recognition since it can determine how much power each app is using, highlighting potential issues. Power usage is broken down into three categories: Low, High, and Very High.
To use Efficiency mode, simply select a Process in Task Manager, then select Efficiency mode from the top bar. You may see a warning message telling you that by turning on Efficiency mode, the process’ priority will become lower.
You can only click on a process rather than an app since Task Manager will display a process and subprocesses, allowing you to discover potentially resource-hungry processes that may be causing your computer to slow down.



